Buying Guide: Choosing a Shockwave Therapy Device for Clinics
- Buying Guide: Choosing a Shockwave Therapy Device for Clinics
- What is a shockwave therapy device and why clinics invest in one
- Clinical indications and evidence for shockwave therapy device use
- Types of shockwave therapy devices: electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, piezoelectric, and radial
- Key technical specs to evaluate in a shockwave therapy device
- Product spotlight: Electromagnetic Focused Shockwave Therapy Machine LGT-2520GP
- Comparing device types and typical clinical use cases
- Operational considerations: workflow, training, and patient experience
- Reimbursement, coding and return on investment (ROI)
- Regulatory, safety and quality considerations
- Case workflows and typical treatment protocols
- Comparing feature sets: a practical checklist for procurement
- Why choose the LGT-2520GP for your clinic?
- Cost comparison example and estimated ROI (illustrative)
- Installation, maintenance and service agreements
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Is focused shockwave therapy safe?
- Can shockwave therapy replace surgery?
- How many sessions do patients usually need?
- Does device technology matter clinically?
- Do patients need anaesthesia?
- How do I evaluate vendors?
- Contact / View product
- References and further reading
Buying Guide: Choosing a Shockwave Therapy Device for Clinics
What is a shockwave therapy device and why clinics invest in one
Shockwave therapy devices deliver acoustic (pressure) waves to soft tissues and bone to relieve pain, promote tissue repair, and reduce inflammation. Clinics purchase a shockwave therapy device to expand non‑invasive treatment options for musculoskeletal conditions (tendinopathies, plantar fasciitis, calcific tendinopathy, and delayed bone healing), to increase patient throughput, and to offer evidence-based conservative care that may reduce referrals for injections or surgery.
Clinical indications and evidence for shockwave therapy device use
High-quality evidence supports extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) for selected conditions. For plantar fasciitis, calcific shoulder tendinopathy, and some chronic tendinopathies, randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews report meaningful pain and function improvements compared with placebo or other conservative care in many studies. However, effectiveness varies by indication, treatment protocol, and device technology, so clinics should match device capabilities to their patient population.
Types of shockwave therapy devices: electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, piezoelectric, and radial
When choosing a shockwave therapy device, understanding the underlying technology is essential. Common device types are:
- Electromagnetic focused: generates a focused pressure field whose focal depth and energy can be precisely controlled — suitable for deeper, focal musculoskeletal lesions.
- Electrohydraulic: uses spark-gap generation and parabolic reflectors to create a focused shock; historically common in lithotripsy and ESWT.
- Piezoelectric: creates focused waves from an array of piezo crystals — high precision, typically lower maintenance.
- Radial pressure wave devices (RPW or radial shockwave): produce unfocused pressure waves that disperse energy superficially and across a wider treatment area — often used for larger superficial regions.
- Energy Flux Density (EFD): expressed in mJ/mm² — determines tissue energy delivered. Higher EFDs are used for calcific deposits and bone healing; lower for pain modulation.
- Focal depth range and adjustability: ability to set depth precisely (e.g., 5–40 mm) allows targeting of specific tissues.
- Focus size: smaller focal zones concentrate energy; larger focal zones distribute energy across tissues.
- Repetition rate (Hz): treatments with optimized rates reduce session time and patient discomfort.
- Pulse count per session and programmability: preset protocols for indications save clinician time and support reproducibility.
- Applicators and coupling: variety of heads (small, large, different materials) increases versatility; good coupling systems prevent energy loss.
- Maintenance, consumables and expected service intervals: downtime affects ROI.
- Staff training: accredited vendor training on energy selection, focal depth, and coupling to ensure safe, effective treatment.
- Treatment time and throughput: average session time is 10–20 minutes; factor in setup, consent and documentation.
- Patient comfort and analgesia: higher EFDs produce more discomfort — some clinics use local anaesthetic selectively, though evidence is mixed about its effect on outcomes.
- Room footprint and electrical requirements: focused units may need dedicated space and appropriate electrical supply. Confirm with vendor technical specs.
- Consumables and maintenance: applicator heads, coupling gels, and periodic servicing impact ongoing costs.
- Check local billing codes and whether payers reimburse for ESWT for the specific diagnosis.
- Estimate ROI using patient volume, expected treatment price per session, number of sessions per course, and maintenance/service costs.
- Consider marketing and referral pathways: offering a proven non‑surgical option may attract referrals and retain patients.
- Regulatory clearance: confirm device has clearance/approval where you practice (e.g., CE marking in Europe, FDA clearance in the U.S., or local regulatory approval).
- Clinical protocols: ensure the vendor provides evidence‑based protocols and training materials.
- Adverse event reporting and safety: inquire about known device risks, contraindications (e.g., pregnancy, coagulation disorders, local infections, tumours), and recommended patient screening.
- Data capture and documentation: devices that log treatment parameters and store protocols support clinical governance and outcome tracking.
- Assessment and informed consent, baseline outcome scores.
- One to three treatment sessions at weekly or biweekly intervals; 1,500–3,000 pulses per session depending on protocol and device.
- Adjust energy (EFD) and focal depth to the lesion; combine with load‑management and physiotherapy.
- Follow-up at 6–12 weeks to assess clinical improvement.
- Is the device focused or radial? Can focal depth be adjusted?
- What is the EFD range and maximum energy available?
- Are preloaded treatment protocols available and editable?
- What applicator heads are included? Are spare heads or consumables required?
- What training and post‑purchase support are offered (on-site training, online modules, refresher courses)?
- Warranty length, service plans, and typical downtime for maintenance.
- Evidence and clinical references from the vendor — are there published clinical studies using the exact device model?
- Regulatory clearances and safety documentation.
- Adjustable electromagnetic focus for targeting at varied depths — increases clinical versatility for deep tendinopathies and calcifications.
- Programmable protocols and likely multiple applicator options (confirm with vendor) to support common indications.
- Focused high‑energy delivery enabling indications that require deeper penetration and focal pressure.
- Vendor training and support pathways to ensure safe implementation and reproducible clinical practice.
- Installation support and room set‑up guidance.
- Planned preventive maintenance intervals and typical service response times.
- Availability and cost of spare parts and applicator heads.
- Software updates and compatibility with clinic IT systems.
- International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment (ISMST) — official site and guidelines: https://www.ismst.org/
- Cochrane Library — systematic reviews on extracorporeal shock wave therapy for musculoskeletal conditions: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/
- National health portals and device regulatory agencies (e.g., NHS, FDA) for local guidance on indications and device clearances: https://www.nhs.uk/, https://www.fda.gov/
- Selected peer-reviewed literature and clinical reviews on ESWT and musculoskeletal indications (search PubMed for Wang CJ and systematic reviews on ESWT): https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Each technology has clinical trade-offs. Focused devices (electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, piezoelectric) reach adjustable depths and higher peak pressures for focal lesions; radial devices are lower cost but work more superficially. When your clinic treats deep tendon insertions, calcifications, or bone non-unions, a focused shockwave therapy device is generally preferable.
Key technical specs to evaluate in a shockwave therapy device
keyword: shockwave therapy device
Focus on these objective metrics when comparing devices:
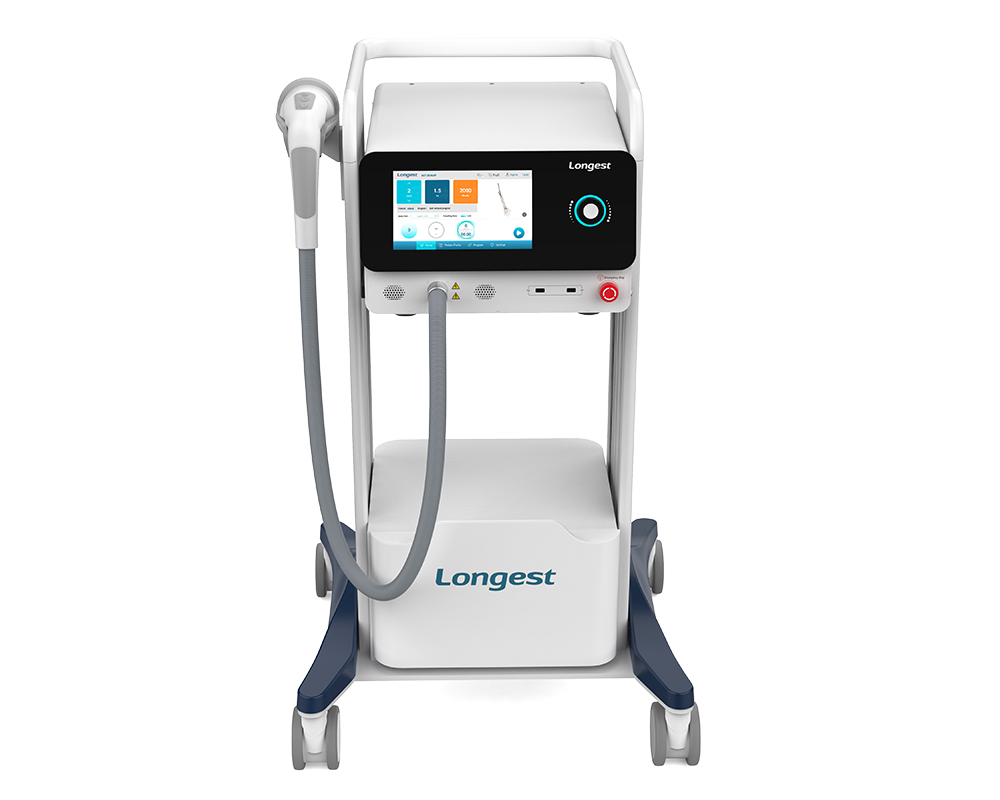
Product spotlight: Electromagnetic Focused Shockwave Therapy Machine LGT-2520GP
The LGT-2520GP incorporates the state-of-the-art Electromagnetic Shockwave technology. This technology gives rise to a pressure field that converges within the adjustable focus at precise depths within particular tissues, attaining the maximum pressure. It is capable of precisely pinpointing the origin of musculoskeletal disorders, efficiently alleviating pain, facilitating tissue repair, and diminishing inflammation. The adjustable focus feature allows medical professionals to customize the treatment according to the specific requirements of each patient and the nature of their condition.
The LGT-2520GP is an example of an electromagnetic focused shockwave therapy device that emphasizes adjustable focal depth and targeted high-energy delivery — features clinics require when treating deeper pathology such as calcific tendinopathy or bone healing indications.
Comparing device types and typical clinical use cases
Below is a practical comparison to help clinics choose the right shockwave therapy device for their caseload. Data reflects typical ranges and clinical tendencies; always verify vendor specifications.
| Device Type | Typical Focal Depth | Typical Energy (EFD) | Best Clinical Uses | >Pros / Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic focused (e.g., LGT-2520GP) | Adjustable, shallow to deep (e.g., 5–40 mm) | Low to high (0.03–0.45 mJ/mm² typical ranges) | Deep tendinopathies, calcific deposits, bone healing | Precise targeting, good depth control; higher cost, requires training |
| Electrohydraulic | Adjustable, focused | Medium to high | Focal deep lesions, established ESWT applications | Powerful; historically bulkier and more maintenance |
| Piezoelectric | Focused, precise | Low to medium | Precise focal lesions, superficial to mid-depth | Accurate focus, low maintenance; sometimes lower maximum energy |
| Radial pressure wave | Superficial (0–2 cm) | Lower (pressure waves, not true high‑energy shockwaves) | Superficial myofascial pain, trigger points, wide areas | Lower cost, easy to use; less effective for deep focal pathology |
Sources for comparative summaries: professional society guidance and systematic reviews listed below.
Operational considerations: workflow, training, and patient experience
keyword: shockwave therapy device
Before purchasing, clinics should plan for:
Reimbursement, coding and return on investment (ROI)
Reimbursement for shockwave therapy varies by country, payer, and indication. Clinics should:
Regulatory, safety and quality considerations
keyword: shockwave therapy device
Important checks before purchasing:
Case workflows and typical treatment protocols
Typical clinical courses vary by indication. Example general approach for chronic tendinopathy:
Protocols should be adapted to device specifications — consult manufacturer guidance (e.g., LGT-2520GP presets) and published trials for specific indications.
Comparing feature sets: a practical checklist for procurement
Use this checklist in vendor discussions when evaluating a shockwave therapy device:
Why choose the LGT-2520GP for your clinic?
The Electromagnetic Focused Shockwave Therapy Machine LGT-2520GP is designed for clinics that need precise, adjustable focal therapy. Key advantages include:
When combined with a robust clinical pathway (patient selection, adjunct physiotherapy, outcome measurement), an electromagnetic focused shockwave therapy device like the LGT-2520GP can expand a clinic’s therapeutic capabilities and align with evidence-based conservative care.
Cost comparison example and estimated ROI (illustrative)
| Item | Focused device (e.g., LGT-2520GP) | Radial device |
|---|---|---|
| Typical purchase price (approx.) | Higher (capital investment) | Lower |
| Average session revenue | Higher for focal indications | Moderate |
| Number of sessions per week (example) | 20–60 (depending on referrals) | 20–60 |
| Estimated break-even (months) | 6–24 (depends on volume and reimbursement) | 4–18 |
Note: These figures are illustrative. Clinics should run a local business case using real local data, reimbursement rates and expected patient throughput.
Installation, maintenance and service agreements
Confirm these vendor commitments before purchase:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is focused shockwave therapy safe?
Yes, when used according to indication-specific protocols and contraindications it is generally safe. Minor adverse effects (transient pain, tenderness, local bruising) are common. Serious complications are rare. Proper training and patient selection reduce risk.
Can shockwave therapy replace surgery?
Shockwave therapy can reduce pain and improve function for many patients and, in some indications, reduce the need for surgery. However, it is not a universal replacement; surgical referral is still appropriate for some structural failures or cases that do not respond to conservative care.
How many sessions do patients usually need?
Typical courses range from 1–6 sessions depending on diagnosis, device, and protocol. Chronic tendinopathies often require 3 sessions at weekly intervals; plantar fasciitis can be effectively treated with 1–3 sessions in some protocols.
Does device technology matter clinically?
Yes. Focused devices (electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, piezoelectric) can reach deeper lesions and deliver concentrated energies; radial devices treat superficial tissue. Match technology to the clinic’s common indications.
Do patients need anaesthesia?
Most treatments are performed without general anaesthesia. Local anaesthetic may be used selectively, although some studies suggest local anaesthesia can blunt therapeutic effects; follow current clinical guidance and device manufacturer recommendations.
How do I evaluate vendors?
Request device specifications, regulatory documentation, peer-reviewed clinical studies using the same model, onsite demos, training programs, service agreements, and references from other clinics.
Contact / View product
To evaluate whether the Electromagnetic Focused Shockwave Therapy Machine LGT-2520GP is right for your clinic, contact our sales and clinical team for a product demo, technical specification sheet, and ROI calculator. Reach out today to schedule an on-site or virtual demonstration and obtain clinical protocols tailored to your patient population.
References and further reading
Note: For device-specific clinical evidence, request peer-reviewed studies and clinical trial data from the manufacturer for the LGT-2520GP.
Wholesale sports recovery manufacturer and supplier
Electrotherapy Devices: Benefits and Risks for Pain Relief
Comprehensive Guide to Active Passive Trainer Price and Benefits in Rehabilitation Equipment
Clinical Evidence for Shockwave Therapy Machines: Studies
LGT-2410S W
How is the quality of the product guaranteed?
Longest medical's rehabilitation bike is made of high-quality materials and undergoes a rigorous quality inspection process to ensure its sturdy structure and stable and reliable performance. The electronic components and transmission system of the device are carefully designed and tested to withstand long-term use and ensure safety and accuracy during use.
2500s plus beauty version
What are the investment benefits of the PowerShocker LGT-2500S Plus?
Favorable price, long lifespan, low maintenance cost, and good after-sales service and technical support.
2500s plus physical therapy version
What are the characteristics of the radial pulse wave therapy machine PowerShocker LGT-2500S Plus?
The PowerShocker LGT-2500S Plus is characterized by compact dimension, easy operation, reliability, and low maintenance.
LGT-233
When should be the MStim Drop LGT-233 applied to a patient?
No matter the stage of foot drop, the MStim Drop LGT-233 can be used for intervention. In the early stage, when patients are bed-bound, the device's train mode can prevent muscle atrophy and conduct strength training. When patients start step training, the walk mode of the MStim Drop LGT-233 can assist. Even if the foot drop is difficult to improve, it can serve as a neuroprosthesis, helping patients walk better and safer.
Electrostatic Oscillation
Who is not suitable to use this device?
It is not recommended for people with metal implants (such as pacemakers), pregnant women, open wounds or severe skin diseases. Before use, if you have any health concerns, it is recommended to consult a professional doctor first.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Pelvic floor rehabilitation LGT-2640AP
The LGT-2640AP Pelvic Floor Magnetic Stimulator is a precision rehabilitation device designed for targeted pelvic floor therapy. Featuring 24 visualized preset protocols (paired with anatomical diagrams), customizable treatment plans, and a pre-adaptation function, it delivers non-invasive, painless stimulation to support postpartum recovery, male pelvic floor rehabilitation, and geriatric pelvic health.

High-Frequency Therapy Device LGT-3500GP(Desktop Design)
LGT-3500GP fits tight spaces without sacrificing performance. Equipped with full TECAR tech, dual tissue-targeting modes, and core safety features, it handles post-op rehab, shallow tissue care, and more—lightweight, durable, and perfect for space-conscious facilities.

High Frequency Therapy Device LGT-3500LP(Upright Design)
The LGT-3500LP has an upright design with plenty of storage and rolling casters for easy mobility. It uses TECAR Therapy, and it has dual CET/RET modes, 300 KHz~1 MHz frequencies, and safety features like real-time temperature monitoring. This gives you precise, efficient treatments for deep tissue repair and pain relief.

Professional 12-Channel Low-Frequency Electrical Stimulation Machine LGT-2320SP
LGT-2320SP is an advanced electrical stimulation sports training station. It leads to multisite high-efficiency strength gain and realizes bilateral balanced development with motor point detection.
Specifically designed for sports medicine professionals, this device is ideal for the treatment and rehabilitation of sports-related injuries. It delivers precise electrical impulses to targeted areas of the body, promoting pain relief, muscle strengthening, and accelerated recovery.
© 2025 Longest Medical. All Rights Reserved. Powered by gooeyun.






LongestMedical
LongestGloba
longest
guangzhou_longest
GzLongest