How to Use a Shockwave Therapy Machine: Protocols & Safety
- How to Use a Shockwave Therapy Machine: Protocols & Safety
- Introduction: why proper use matters for a shockwave therapy machine
- Understanding device types: focused vs radial shockwave therapy machine
- How shockwaves work: basic mechanism for a shockwave therapy machine
- Key treatment parameters to set on a shockwave therapy machine
- General clinic workflow before using a shockwave therapy machine
- Patient positioning and target mapping for effective shockwave therapy machine use
- Specific treatment protocols for common indications using a shockwave therapy machine
- Plantar fasciitis protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
- Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
- Achilles and patellar tendinopathy protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
- Calcific shoulder (rotator cuff) protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
- Bone healing and non-union protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
- Device comparison: focused vs radial shockwave therapy machine
- Safety checklist before delivering shockwave therapy machine treatment
- Contraindications and precautions for a shockwave therapy machine
- Managing pain and adverse effects from a shockwave therapy machine
- Combining shockwave therapy machine with rehabilitation
- Maintenance, calibration and staff training for a shockwave therapy machine
- Outcome expectations and timeline with a shockwave therapy machine
- Documentation and billing considerations when using a shockwave therapy machine
- Practical tips to improve patient comfort during shockwave therapy machine sessions
- Longest Medical — company strengths and shockwave product advantages
- Longest’s key product advantages including its shockwave therapy machine
- Sample comparison of Longest Medical product applications
- FAQ — common questions about using a shockwave therapy machine
How to Use a Shockwave Therapy Machine: Protocols & Safety
Introduction: why proper use matters for a shockwave therapy machine
Using a shockwave therapy machine correctly maximizes clinical benefit and minimizes risk. This guide covers device types (focused vs radial), evidence-informed protocols for common musculoskeletal and soft-tissue conditions, safety and contraindications, setup and maintenance, and practical tips to improve patient comfort and outcomes. The language is kept practical and clinically relevant for therapists, clinicians, and facility managers considering or using shockwave devices.
Understanding device types: focused vs radial shockwave therapy machine
There are two main types of shockwave therapy machines: focused shockwave and radial shockwave (rESWT). Focused shockwave delivers concentrated energy to a defined focal point, useful for deeper targets. Radial shockwave disperses pressure over a broader, more superficial area and is often used for tendinopathies near the skin. Choosing the correct shockwave therapy machine type is the first step to an effective protocol.
How shockwaves work: basic mechanism for a shockwave therapy machine
Shockwaves are high-energy acoustic pulses that induce mechanical stress in tissues, triggering biological responses: increased blood flow, neovascularization, modulation of pain receptors, and stimulation of tissue regeneration. The effects depend on energy flux density (EFD), pulse number, and delivery frequency — parameters clinicians adjust on their shockwave therapy machine to match the clinical goal.
Key treatment parameters to set on a shockwave therapy machine
When programming a shockwave therapy machine, main parameters are energy (EFD in mJ/mm2 for focused; pressure in bar for radial), number of pulses, frequency (Hz), and applicator size. Typical ranges used in practice: focused EFD 0.03–0.60 mJ/mm2, radial pressure 1–4 bar, pulses 1000–4000 per session, and frequency 1–15 Hz. Start with lower energy for patient tolerance and increase based on response and evidence-based protocols.
General clinic workflow before using a shockwave therapy machine
Begin with a thorough assessment (history, exam, imaging when needed), informed consent, and documentation of baseline pain and function. Explain expected sensations, possible transient side effects, and post-session advice. Check the shockwave therapy machine calibration, handpiece condition, and applicator coupling. Prepare coupling gel and position the patient comfortably to access target tissue.
Patient positioning and target mapping for effective shockwave therapy machine use
Proper positioning and mapping minimize wasted energy and discomfort. Identify the point of maximal tenderness and use anatomical landmarks or ultrasound to target the lesion. For tendon pathologies, angle the applicator longitudinally along fibers. For plantar fascia, apply under the heel with foot supported. Use light continuous movement for radial devices or a focused stationary approach for precise focal lesions.
Specific treatment protocols for common indications using a shockwave therapy machine
Below are practical, commonly used protocols. These are general guidance — individualize by patient response, device model, and current evidence.
Plantar fasciitis protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
Common protocol: focused EFD 0.08–0.25 mJ/mm2 or radial 2–3 bar, 1500–3000 pulses per session, 1–2 sessions per week, total 3–4 sessions. Outcomes often emerge after 4–12 weeks. Avoid local corticosteroid injection within two weeks before or after high-energy focused treatment.
Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
Typical settings: radial 2–3 bar or focused EFD 0.08–0.20 mJ/mm2, 1500–2500 pulses, weekly sessions for 3–4 weeks. Combine with eccentric loading exercises for best long-term results.
Achilles and patellar tendinopathy protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
For mid-portion Achilles or patellar tendinopathy: radial 2–4 bar or focused 0.08–0.25 mJ/mm2, 2000–3000 pulses, weekly sessions for 3–6 weeks. Incorporate progressive loading programs (eccentric/concentric) starting after the first week as tolerated.
Calcific shoulder (rotator cuff) protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
Calcific tendinopathy may require higher-energy focused shockwave: EFD 0.2–0.4 mJ/mm2, 1500–2000 pulses per session, one or two sessions spaced 1–2 weeks apart. Imaging follow-up can document calcium fragmentation and clinical improvement. Note: higher energies can be painful — local anesthesia may be considered, but evidence about anesthesia effect varies.
Bone healing and non-union protocol for a shockwave therapy machine
For bone non-union, protocols are higher energy and often single or few sessions: focused EFD typically 0.3–0.6 mJ/mm2, 2000–4000 pulses per session. This indication is generally performed in orthopedic settings with imaging guidance and under clear protocols.
Device comparison: focused vs radial shockwave therapy machine
Below is a concise comparison table to help choose the right device type for common clinical needs.
| Feature | Focused Shockwave Machine | Radial Shockwave Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Concentrated acoustic focal point | Pressure wave spreading out from applicator |
| Typical penetration | Deeper (up to ~6–12 cm depending on device) | Superficial to mid-depth (up to ~3–4 cm) |
| Energy unit | EFD (mJ/mm²) | Pressure (bar) or Joules (manufacturer-dependent) |
| Common indications | Calcific tendinopathy, deep lesions, bone healing | Tendinopathies (patellar, Achilles, lateral epicondylitis), plantar fasciitis |
| Pain during treatment | Can be higher; local anesthesia sometimes used | Usually better tolerated; lower peak pain |
| Typical pulses per session | 1000–4000 | 1000–4000 |
Safety checklist before delivering shockwave therapy machine treatment
Before each session: confirm indication and absence of contraindications (pregnancy, untreated malignancy at site, infection, over open growth plates, acute thrombosis). Review anticoagulant status — shockwaves can cause transient subcutaneous bleeding in anticoagulated patients. Ensure handpiece is intact, coupling gel is used, and emergency contacts are available. Document baseline pain and function scores.
Contraindications and precautions for a shockwave therapy machine
Absolute contraindications commonly include pregnancy, active infection or malignancy in the treatment area, and areas over major blood vessels with acute thrombosis. Relative contraindications: anticoagulation, uncontrolled diabetes, neuropathy with reduced sensation, and implanted electronic devices (consult manufacturer guidance). Avoid treatment over epiphyseal plates in growing children.
Managing pain and adverse effects from a shockwave therapy machine
Adverse effects are usually mild and transient: local pain, bruising, swelling, or numbness. Analgesia with paracetamol or short-term NSAIDs is acceptable, but avoid high-dose local anesthetic before some focused treatments because anesthesia may attenuate beneficial effects according to some studies. Monitor and document any adverse events and adjust energy or session frequency if needed.
Combining shockwave therapy machine with rehabilitation
Shockwave therapy is most effective when combined with targeted rehabilitation: progressive loading, stretching, and biomechanical correction. Start or continue an exercise program tailored to the pathology; use shockwave to accelerate biological healing while rehab addresses function, strength, and movement patterns.
Maintenance, calibration and staff training for a shockwave therapy machine
Keep the shockwave therapy machine in line with manufacturer-recommended maintenance: regular calibration, handpiece inspections, and software updates. Train staff thoroughly on device settings, contraindications, and emergency procedures. Document competency and maintain a usage log for quality control and regulatory compliance.
Outcome expectations and timeline with a shockwave therapy machine
Outcome timelines vary: some patients feel improvement within 1–3 weeks; many show significant improvement after 6–12 weeks. For chronic tendinopathies, expect progressive improvement and combine with rehab. Repeat sessions depend on response; common course is 3–6 sessions over 3–6 weeks. If there's no improvement after a recommended course, re-evaluate diagnosis and consider alternative therapies.
Documentation and billing considerations when using a shockwave therapy machine
Document indication, baseline measures, device settings (EFD/pressure, pulses, frequency), consent, and adverse effects. Coding and reimbursement vary by region and payer — check local billing rules for shockwave therapy machine procedures and include objective outcome measures when possible (e.g., VAS, functional scores).
Practical tips to improve patient comfort during shockwave therapy machine sessions
Tips: start at lower energy and gradually increase, use short breaks for very painful areas, apply cooling afterward if needed, and explain sensations and expected timeline. For anxious patients, distraction techniques or light topical analgesic patches (with caution) can help. Ensure an efficient clinic flow to reduce patient anxiety and waiting time.
Longest Medical — company strengths and shockwave product advantages
Founded in 2000, Longest Medical is a leading global rehabilitation and aesthetic solutions company, focusing on non-invasive medical solutions. Longest’s experience gives it strengths in integrated product lines and quality manufacturing. Their shockwave therapy machines and related devices are designed for clinical versatility and durability, supporting physical therapy, neurological rehab, postoperative recovery, veterinary treatment, and medical aesthetics.
Longest’s key product advantages including its shockwave therapy machine
Advantages of Longest Medical include: long industry experience, diversified non-invasive therapy portfolio, global regulatory awareness, and strong after-sales support. Their shockwave therapy machine and focused shockwave machines offer adjustable energy ranges, user-friendly interfaces, and interchangeable applicators for tailored treatments. Other Longest products — electrical muscle stimulation machines, air relax compression systems, active-passive trainers, compression therapy machines, DVT prevention devices, lymphatic massage devices, and pressotherapy machines — complement shockwave therapy by offering combined treatment pathways for faster rehabilitation and improved patient outcomes.
Sample comparison of Longest Medical product applications
The table below shows common applications and advantages of Longest’s related devices for a comprehensive rehabilitation approach.
| Product | Primary Use | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Shockwave therapy machine | Musculoskeletal pain, tendinopathies, calcific lesions | Adjustable energy, deep and superficial options, clinical protocols |
| Focused shockwave therapy machine | Deep calcific lesions, bone healing | Precise focal delivery, higher EFD range |
| Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) | Muscle re-education, pain modulation | Programmable protocols, complementary to shockwave |
| Air Relax compression / Pressotherapy | Lymphedema, venous insufficiency, recovery | Sequential compression to enhance lymphatic/venous return |
| Active-passive trainer | Joint mobility and early-stage rehab | Controlled ROM and assisted exercise for recovery |
| DVT medical device | Thrombosis prevention post-op or immobility | Effective compression cycles for prophylaxis |
| Lymphatic massage device | Lymphedema management, detoxification | Comfortable protocols with clinical settings |
FAQ — common questions about using a shockwave therapy machine
Q: Is shockwave therapy machine treatment painful?
A: Most patients report a transient sharp or aching sensation during treatment. Pain is usually brief and manageable; clinicians start at lower energy and titrate up for tolerance.
Q: How many sessions with a shockwave therapy machine are typically needed?
A: Typical courses are 3–6 sessions spaced 1 week apart, though some conditions may require fewer or additional sessions depending on response.
Q: Can a shockwave therapy machine be used with anticoagulant therapy?
A: Use caution. Anticoagulated patients have higher bruising risk; consult with the prescribing physician and consider lower energies or alternative treatments.
Q: Are shockwave therapy machines safe for children?
A: Avoid treating over open growth plates in children; use is typically restricted and must follow pediatric specialists’ guidance.
Q: Does anesthesia affect the effectiveness of a shockwave therapy machine?
A: For some focused treatments, local anesthesia may reduce pain but could attenuate biological responses. Follow current evidence and manufacturer guidance when considering anesthesia.
Q: What aftercare is recommended following shockwave therapy machine treatment?
A: Advise relative rest for 24–48 hours, avoid intense activity for a few days, continue prescribed rehab exercises, and use paracetamol if needed for discomfort. Avoid icing directly over the treated area if you aim to support local inflammation-driven healing.
Q: When should I refer a patient after shockwave therapy machine failure?
A: If there is no clinical improvement after an evidence-based course (typically 3–6 sessions) or symptoms worsen, re-evaluate diagnosis, consider imaging, and refer to appropriate specialists (orthopedics, pain medicine).
Using a shockwave therapy machine effectively requires appropriate device selection, evidence-informed protocols, clear patient communication, and a combined rehab approach. When integrated properly, shockwave therapy can be a powerful non-invasive tool to accelerate recovery and reduce chronic pain.
Active Passive Trainer Cost in Japan: Complete Price Guide & Buying Tips
Active Passive Trainer Cost in Mexico: Buyer’s Guide for Clinics and Rehab Centers
Wholesale electrical muscle stimulation device manufacturer and supplier
Wholesale anti dvt machine manufacturer and supplier
2500X
Is OEM/ODM service available?
Yes. Contact us for more details. We offer professional OEM/ODM services.
LGT-2410S W
How is the quality of the product guaranteed?
Longest medical's rehabilitation bike is made of high-quality materials and undergoes a rigorous quality inspection process to ensure its sturdy structure and stable and reliable performance. The electronic components and transmission system of the device are carefully designed and tested to withstand long-term use and ensure safety and accuracy during use.
Combination Therapy
When is combination therapy used?
This device is intended for soft - tissue pain relief, muscle recovery, and re - education. It can be applied to alleviate musculoskeletal pain, reduce muscle spasms and tension, enhance blood circulation, facilitate healing, and restore muscle functions.
LGT-233
Does your product come with a warranty?
Yes, we're committed to delivering quality products and excellent after-sales service to enhance your overall experience.
Company
How is the company's cooperation with the international market?
In 2012, the International Sales Department was established, and cooperative relationships have been established with distributors and agents in more than 80 countries around the world. The products are widely used in overseas medical institutions and are highly recognized. We actively participate in international academic exchange activities to promote resource sharing.
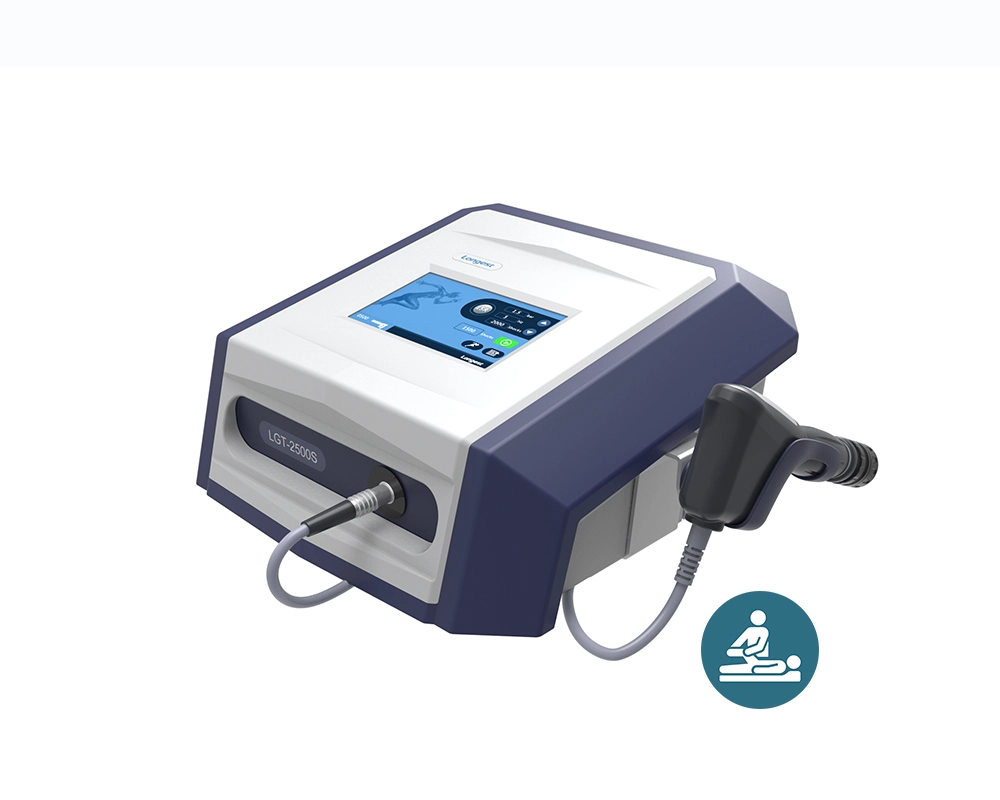
Electrical Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Device PowerShocker LGT-2500S
The LGT-2500S is a portable, tabletop extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) device. It effectively stimulates the healing of troublesome tissue, alleviates pain, and non-invasively supports the recovery of the patient's tissue. It is a completely natural and drug-free option for various conditions in physiotherapy, veterinary medicine, and aesthetic medicine.
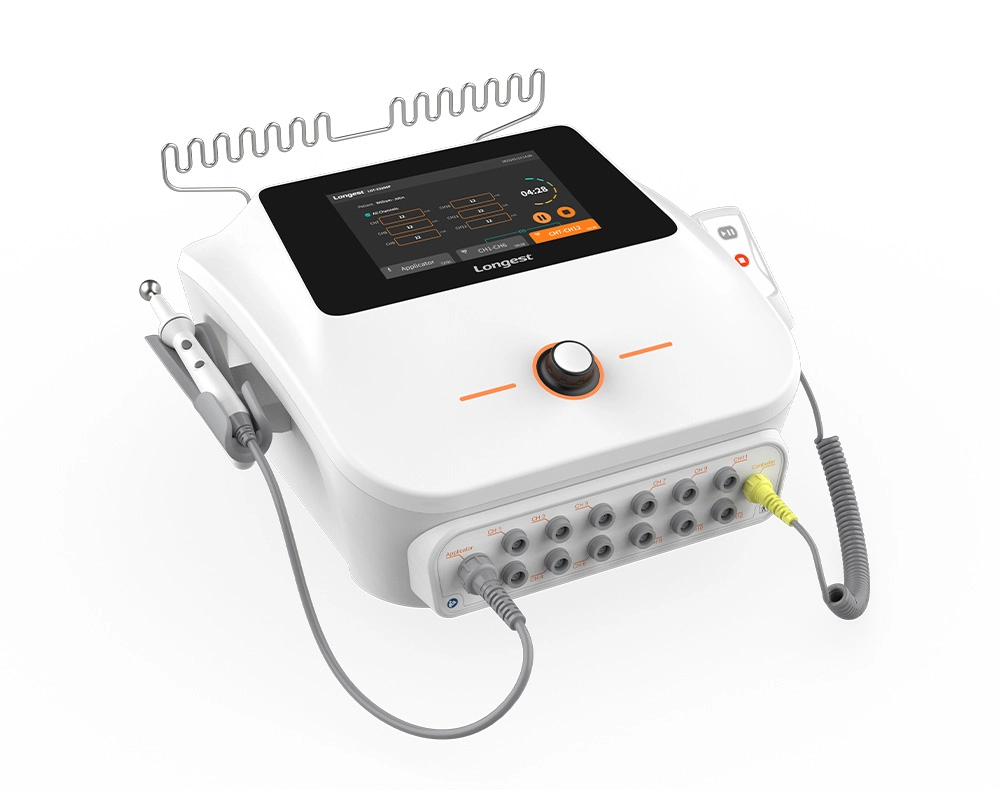

Professional 12-Channel Low-Frequency Electrical Stimulation Machine LGT-2320SP
LGT-2320SP is an advanced electrical stimulation sports training station. It leads to multisite high-efficiency strength gain and realizes bilateral balanced development with motor point detection.
Specifically designed for sports medicine professionals, this device is ideal for the treatment and rehabilitation of sports-related injuries. It delivers precise electrical impulses to targeted areas of the body, promoting pain relief, muscle strengthening, and accelerated recovery.
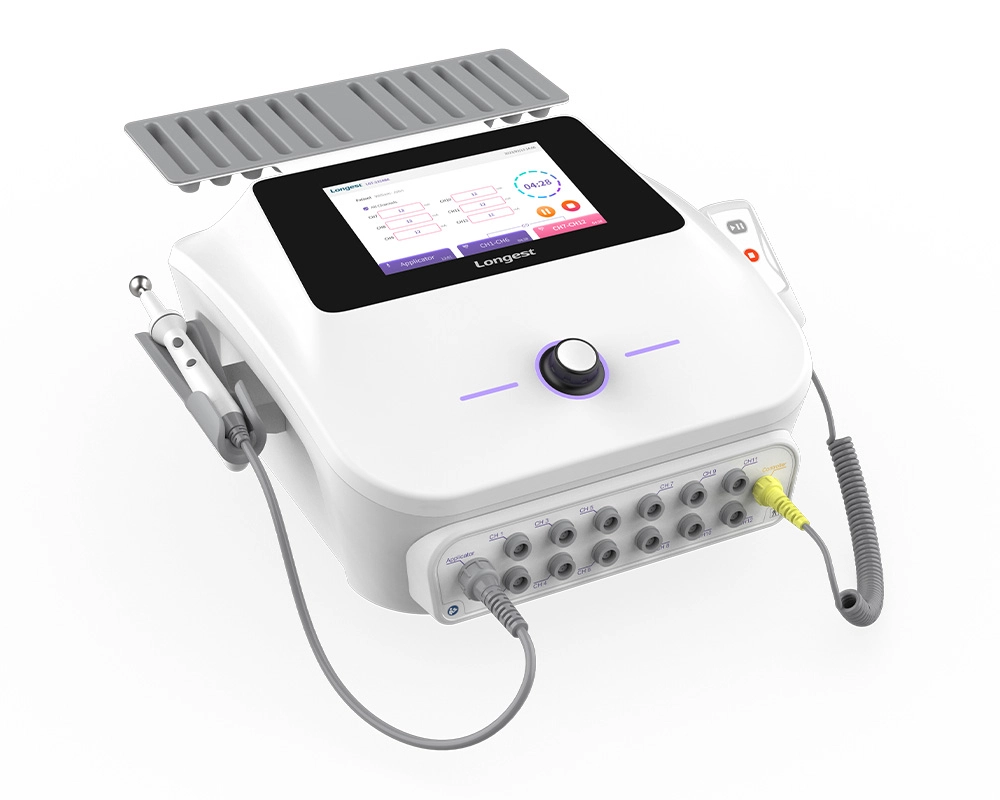

Professional 12-Channel Low-Frequency Electrical Stimulation Machine LGT-2320BE
The LGT-2320BE is an advanced EMS machine, leveraging the power of low-frequency electrical stimulation therapy to achieve remarkable results in body sculpting.
It not only efficiently contours and tones the body but also actively promotes muscle relaxation, relieving tension and soreness. Moreover, it plays a significant role in enhancing skin elasticity, rejuvenating the skin's appearance and suppleness.
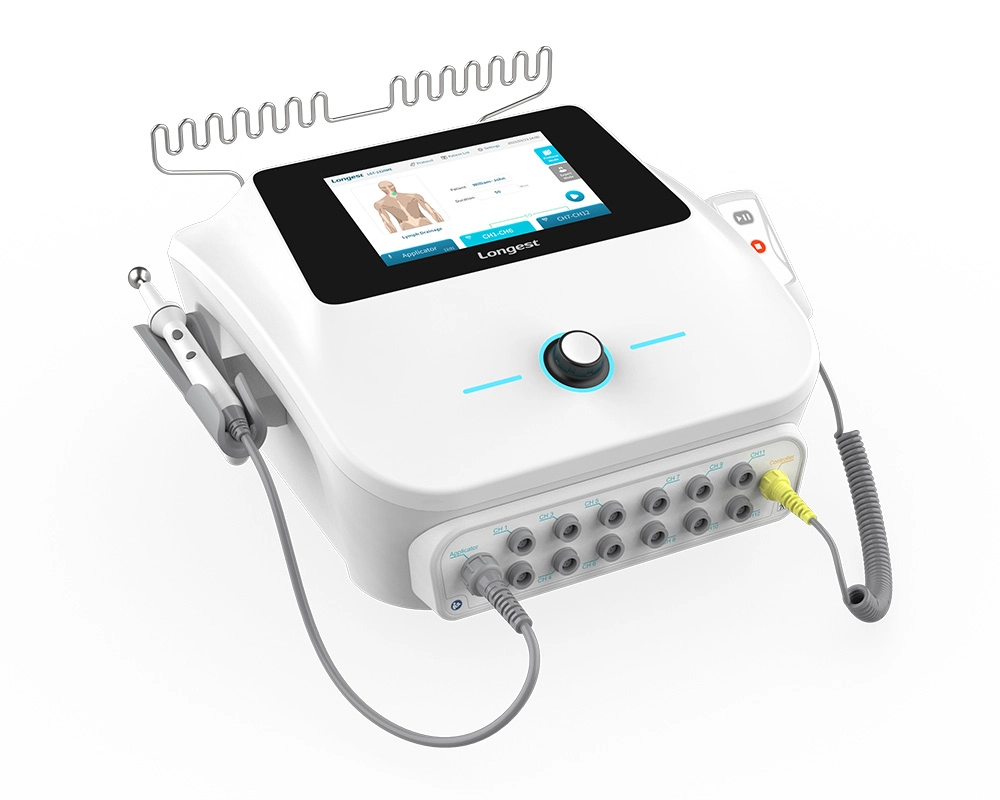
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation NMES Machine LGT-2320ME
The LGT-2320ME, a portable electro-stimulation therapy device, is mainly composed of the main unit, a hand switch, a pen electrode controller, and diverse types of electrodes.
It has the capacity to supply three channel groups (CH1-CH6, CH7-CH12, and the Applicator channel) with either TENS or NMES current. Specifically engineered for utilization in hospitals and clinics, this device effectively assists patients in reclaiming lost muscle strength and expedites recovery times, consequently enhancing the overall standard of patient care and bringing about more satisfactory rehabilitation outcomes.
© 2025 Longest Medical. All Rights Reserved. Powered by gooeyun.







LongestMedical
LongestGloba
longest
guangzhou_longest
GzLongest