How Electrotherapy Devices Work: A Simple Guide
- How Electrotherapy Devices Work: A Simple Guide
- What are electrotherapy devices?
- Basic principles: how electrical signals affect nerves and muscles
- Key components of electrotherapy devices
- Common types of electrotherapy devices and their clinical uses
- Comparison table: common electrotherapy modalities
- What the evidence says about effectiveness
- Safety, contraindications, and best practices
- How to choose the right electrotherapy device (buying guidance)
- Practical tips for effective treatment with electrotherapy devices
- Longest Medical: a partner in non-invasive rehabilitative and aesthetic electrotherapy solutions
- Why Longest Medical is relevant to electrotherapy device buyers
- Key Longest Medical products related to electrotherapy
- How Longest’s electrotherapy devices support clinical workflows
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Are electrotherapy devices safe for home use?
- Can electrotherapy devices cure chronic pain?
- How quickly do patients see results?
- What should clinicians look for when buying electrotherapy devices?
- Contact and product information
- References
How Electrotherapy Devices Work: A Simple Guide
What are electrotherapy devices?
Electrotherapy devices are medical and therapeutic instruments that deliver controlled electrical energy through the skin to modify nerve or muscle activity, reduce pain, improve circulation, or assist rehabilitation. Commonly used in clinics, hospitals, sports medicine, and home care, electrotherapy devices include transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), electrical muscle stimulation (EMS/NMES), interferential current (IFC) units, and low-level microcurrent machines. These devices can be intended for pain control, muscle re-education, edema reduction, or drug delivery (iontophoresis), and are increasingly available both as professional equipment and consumer products. Understanding how they work helps clinicians and patients choose safe, effective options for treatment.
Basic principles: how electrical signals affect nerves and muscles
Electrotherapy devices use a few basic electrical parameters to produce clinical effects: current type (direct vs. alternating), pulse width (duration of each electrical pulse), frequency (pulses per second, Hz), amplitude (intensity), and waveform shape. When electrical pulses pass through electrodes placed on the skin, they depolarize sensory or motor nerves depending on intensity and frequency. Low-intensity stimulation can activate large-diameter sensory fibers and gate pain signals at the spinal cord (the gate control theory). Higher intensities recruit motor fibers, causing muscle contraction useful for strengthening, preventing atrophy, or retraining neuromuscular control. Pulse frequency and pattern affect muscle fatigue and the quality of contraction. Manufacturers calibrate devices to allow clinicians to select protocols that match therapeutic goals.
Key components of electrotherapy devices
Most electrotherapy devices share basic hardware: a power source and generator, user controls (to set intensity, frequency, pulse width, and mode), cables, and electrodes. Electrodes come in reusable or single-use forms, often made of conductive silicone or adhesive pads with a hydrogel interface to ensure good contact and reduce skin irritation. Advanced devices include multi-channel outputs allowing simultaneous, independent treatment areas, pre-programmed treatment protocols, safety cutoffs, and digital displays. Portable designs prioritize battery life and usability for patients who require home therapy, while clinic-grade units emphasize versatility, clinical features, and regulatory compliance for medical use.
Common types of electrotherapy devices and their clinical uses
Understanding the main device types helps match treatment to goals. Below are commonly used electrotherapy devices and typical clinical purposes:
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Primarily for pain relief (acute and chronic). Uses sensory-level stimulation to modulate pain signaling.
- Electrical Muscle Stimulation / Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (EMS/NMES): Induces visible muscle contractions for strength training, prevention of atrophy, and neuromuscular re-education after injury or surgery.
- Interferential Current (IFC): Uses two medium-frequency currents that intersect to create a low-frequency therapeutic effect in deeper tissues; often used for pain and swelling.
- High-Voltage Pulsed Current (HVPC): Short, high-voltage pulses used in wound healing and edema management.
- Microcurrent Therapy: Very low amplitude currents claimed to support tissue healing and cellular repair; used in wound care and some pain protocols.
- Iontophoresis: Uses direct current to drive charged medication through the skin (local drug delivery).
Comparison table: common electrotherapy modalities
The following table summarizes key features and typical clinical uses of major modalities:
| Modality | Typical frequency / pulse | Main clinical uses | Comfort / patient sensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| TENS | 1–150 Hz (sensory-level) | Pain relief (acute & chronic) | Tingling, comfortable |
| EMS / NMES | 20–50 Hz (motor-level) | Muscle strengthening, re-education | Visible contraction, may be strong |
| IFC | 4000 Hz carrier; beat frequency 1–150 Hz | Deeper pain, swelling control | Sensation often milder than TENS |
| HVPC | Pulsed, high voltage | Wound healing, edema | Sharp or prickling at times |
| Microcurrent | Microamp-level, low frequency | Tissue repair, inflammation | Often imperceptible |
Source: Clinical rehabilitation guidelines and device manufacturer specifications (see references).
What the evidence says about effectiveness
Clinical studies and systematic reviews show mixed but often positive results for electrotherapy devices, depending on indication and device type. TENS has substantial clinical use for pain relief, though response varies between patients and protocols. NMES is effective for muscle strengthening and preventing post-operative atrophy when appropriately applied. Evidence for microcurrent and some advanced modalities is more limited and depends on study quality. In practice, electrotherapy is often used as part of a multimodal rehabilitation plan rather than as a standalone cure. When selecting devices, clinicians look for peer-reviewed evidence, appropriate regulatory clearance (e.g., FDA, CE), and alignment with clinical goals.
Safety, contraindications, and best practices
Electrotherapy devices are generally safe when used correctly, but they carry contraindications and risks that must be managed. Absolute contraindications commonly include: implanted electronic devices (pacemakers, defibrillators), active malignancy at the treatment site, and application across the trunk of pregnant women. Caution is required near the eyes, over carotid sinuses, and on broken skin unless the modality is intended for wound care. Proper electrode placement, skin preparation, progressive intensity titration, and monitoring for burns or skin irritation are essential. Clinicians should follow manufacturer instructions, document device settings, and provide clear home-use education when patients self-administer treatments.
How to choose the right electrotherapy device (buying guidance)
Whether you are a clinician looking to equip a practice or a patient seeking an at-home solution, choosing electrotherapy devices for sale requires evaluating clinical purpose, regulatory status, features, and cost. Key considerations:
- Intended use: pain relief (TENS) vs. muscle strengthening (NMES) vs. wound care (HVPC).
- Regulatory clearance: FDA 510(k) or CE marking for medical devices suggests appropriate safety and performance checks.
- Adjustability and protocols: adjustable amplitude, frequency, and pulse width; pre-set clinical programs can increase ease of use.
- Electrode quality and availability: reusable vs. single-use, cost, and skin compatibility.
- Portability and battery life for home-use devices.
- Service, warranty, and training offered by the manufacturer or distributor.
Practical tips for effective treatment with electrotherapy devices
To maximize benefit and safety:
- Start with evidence-based protocols and adjust to patient feedback.
- Document exact device settings and electrode placement for reproducibility.
- Combine electrotherapy with exercise, manual therapy, and education for best rehabilitation outcomes.
- Train patients thoroughly if providing home-use devices and supply clear written instructions for use, cleaning, and electrode replacement.
Longest Medical: a partner in non-invasive rehabilitative and aesthetic electrotherapy solutions
Founded in 2000, Longest Medical is a leading global rehabilitation and aesthetic solutions company focusing on non-invasive medical solutions. Longest’s product portfolio spans shock wave therapy, compression therapy, electrotherapy, electrostatic oscillation therapy, cryotherapy, ultrasound therapy, and active-passive trainers. These product lines provide comprehensive equipment solutions for physical therapy, neurological rehabilitation, postoperative recovery, veterinary diagnosis and treatment, medical aesthetics, and related fields.
Why Longest Medical is relevant to electrotherapy device buyers
As clinicians evaluate electrotherapy devices for sale, Longest Medical brings several competitive strengths:
- Broad product range: from electrical muscle stimulation machines to complementary modalities such as shockwave and compression therapy that support multimodal rehabilitation plans.
- Clinical focus: products designed for rehabilitation, neurology, postoperative recovery, and aesthetics — making them suitable for clinics seeking integrated solutions.
- Global experience: operating since 2000 with international distribution and clinical partnerships that support local adoption and training.
- R&D and quality: emphasis on non-invasive device engineering, safety features, and service/warranty structures appropriate for medical settings.
Key Longest Medical products related to electrotherapy
Highlighted product lines and core competencies include:
- Shockwave therapy machine & focused shockwave therapy machine — for musculoskeletal and aesthetic applications where mechanical stimulation complements electrotherapy.
- Electrical muscle stimulation machine (EMS/NMES) — for muscle strengthening, neuromuscular re-education, and postoperative rehabilitation.
- Air Relax compression & compression therapy machine — for lymphedema and venous insufficiency management, often used together with electrotherapy strategies.
- Active passive trainer — for assisted movement training in neurological and orthopedic rehabilitation.
- DVT medical device — devices designed to prevent deep vein thrombosis, relevant in postoperative care settings.
- Lymphatic massage device & Pressotherapy machine — for lymphatic drainage and post-aesthetic recovery.
How Longest’s electrotherapy devices support clinical workflows
Longest’s electrotherapy products are typically built to integrate into therapy pathways: multi-channel outputs for treating multiple muscles, pre-set protocols to reduce clinician setup time, and safety features for patient comfort. For clinics seeking comprehensive rehabilitation equipment, Longest’s combined product lines allow clinicians to create multimodal programs (for example, combining NMES with compression and shockwave therapy) tailored to patient recovery goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are electrotherapy devices safe for home use?
Many devices, particularly consumer-grade TENS units, are safe for home use when used according to manufacturer instructions and after professional guidance. Patients with pacemakers, epilepsy, or pregnancy should not use these devices without clinician approval. Home-use devices should carry appropriate regulatory markings (e.g., FDA clearance for medical devices where required).
Can electrotherapy devices cure chronic pain?
Electrotherapy can provide meaningful pain relief for many patients but is not a guaranteed cure. It is most effective as part of a comprehensive plan that includes exercise, manual therapy, behavioral strategies, and sometimes medication. Individual response varies and should be monitored regularly.
How quickly do patients see results?
Some patients report immediate pain relief with modalities like TENS, while muscle strengthening with NMES requires weeks of consistent application to see measurable gains. Wound healing or tissue-repair effects from microcurrent or HVPC may take longer and depend on underlying health factors.
What should clinicians look for when buying electrotherapy devices?
Look for devices with appropriate regulatory clearances, clinical evidence supporting intended uses, adjustable parameters, quality electrodes, technical support, and warranties. Consider how the device will integrate with your clinic’s workflows and whether it supports multi-modal rehabilitation programs.
Contact and product information
To learn more about electrotherapy devices or to discuss clinical applications and purchasing options, contact Longest Medical customer service or view their product catalog. Professional support, training, and device demonstrations are often available to help match the right electrotherapy devices to your clinical needs.
References
- NHS: Guidance on TENS and electrical stimulation for pain management and rehabilitation.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Information on electrical stimulation devices and regulatory considerations.
- Cochrane Library / Systematic reviews on TENS and electrotherapy modalities for pain management.
- American Physical Therapy Association (APTA): Clinical resources and practice guidance on electrotherapy in rehabilitation.
- Peer-reviewed rehabilitation and sports medicine literature summarizing EMS/NMES and IFC clinical effectiveness.
Note: For product-specific specifications, clinical protocols, or regulatory documentation, consult device manufacturer literature and official regulatory bodies.
Treatment Protocols: Best Practices Using LGT-2500X
Top 10 medical device Manufacturers and Supplier Brands
TENS vs EMS: Choosing the Right Electrotherapy Device
Wholesale dvt machine manufacturer and supplier
Combination Therapy
Can the ultrasound modality be used separately?
Yes. The system features a modular design, allowing the ultrasound module to be used independently. It is compact, lightweight, and battery - powered, making it an excellent choice for mobile healthcare services.
Cryotherapy
What are the differences between Whole - body Cryotherapy and Localized Cryotherapy?
Whole - body cryotherapy offers systemic benefits, ideal for general pain relief, athletic recovery, or body slimming. Localized cryotherapy targets specific injuries or areas, providing focused pain relief and reducing inflammation.
LGT-2500F Copywriter - Medical Beauty Edition
Can treatment plans be customized to meet patient needs?
Absolutely. Treatment plans can be personalized for each patient based on a professional diagnosis of their condition and an understanding of their responses. Moreover, practitioners can save each patient's preferred parameters for convenient access in the future. The system is capable of storing up to 5,000 patient files.
LGT-2900EUV
Does the device support multi-language operation?
Yes, the LGT-2900 series supports multi-language software interfaces (such as English, Spanish, etc.), which can be switched through system settings, making it suitable for medical personnel in different regions.
2510A physical therapy
Can shockwave treatment be combined with other therapies?
Shockwave treatment can be combined with a variety of therapies. For example, when combined with physical therapies such as electrotherapy and laser, it can improve circulation, repair tissues, and relieve pain. It can also be combined with rehabilitation therapies such as rehabilitation training and deep muscle massage to accelerate the patient's rehabilitation process and improve the quality of life. However, the specific treatment plan should be formulated according to the specific condition and individual differences of the patient.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation LGT-2660AP/BP
The LGT-2660 Series Electromagnetic Stimulator for Musculoskeletal Pain is an advanced rehabilitation device engineered to address a wide range of musculoskeletal pain conditions and associated dysfunctions. Operating on the principle of electromagnetic induction, it generates induced currents to regulate neuromuscular function while delivering deeply penetrating energy—this energy transcends superficial tissues to act directly on muscles, joints, and bones. For both acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain, it provides a safe, efficient, and medication-free new solution.
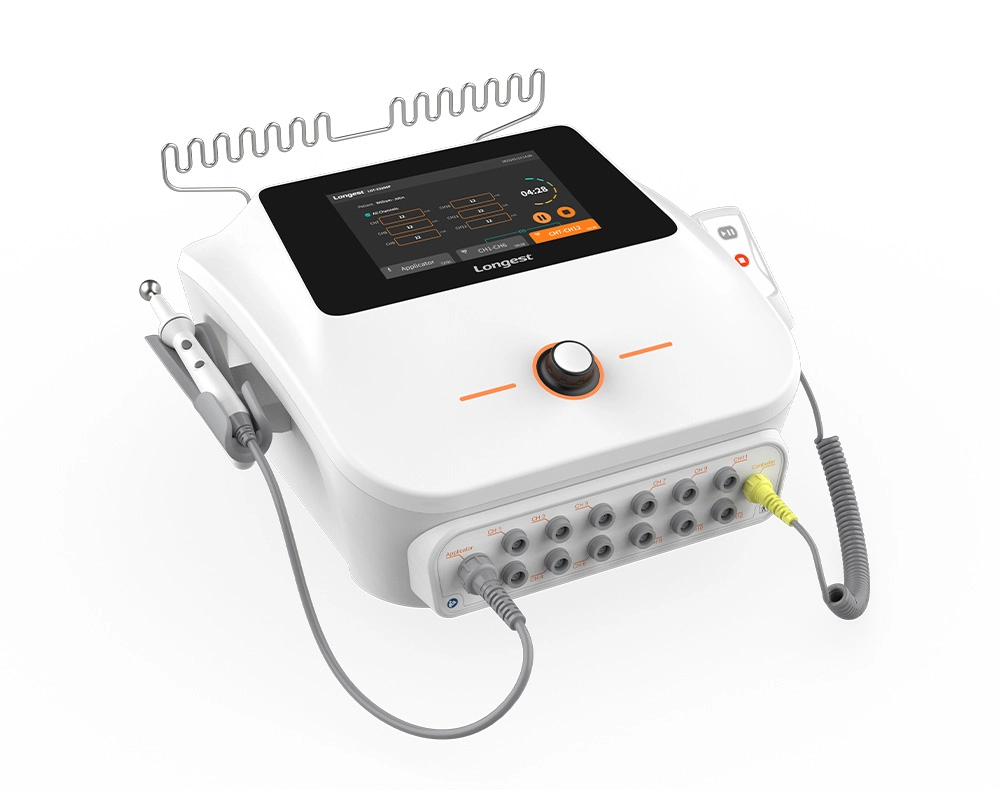

Professional 12-Channel Low-Frequency Electrical Stimulation Machine LGT-2320SP
LGT-2320SP is an advanced electrical stimulation sports training station. It leads to multisite high-efficiency strength gain and realizes bilateral balanced development with motor point detection.
Specifically designed for sports medicine professionals, this device is ideal for the treatment and rehabilitation of sports-related injuries. It delivers precise electrical impulses to targeted areas of the body, promoting pain relief, muscle strengthening, and accelerated recovery.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Pelvic floor rehabilitation LGT-2640AP
The LGT-2640AP Pelvic Floor Magnetic Stimulator is a precision rehabilitation device designed for targeted pelvic floor therapy. Featuring 24 visualized preset protocols (paired with anatomical diagrams), customizable treatment plans, and a pre-adaptation function, it delivers non-invasive, painless stimulation to support postpartum recovery, male pelvic floor rehabilitation, and geriatric pelvic health.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Body Shaping LGT-2650BP
The LGT-2650BP is a premium unisex body contouring device. Powered by high-intensity magnetic stimulation, it induces intense muscle contractions—effectively boosting muscle tone while reducing stubborn fat deposits. It is widely suited for weight management, body shaping, and individuals with excess weight alike.
© 2025 Longest Medical. All Rights Reserved. Powered by gooeyun.






LongestMedical
LongestGloba
longest
guangzhou_longest
GzLongest