World Lymphedema Day: Everything You Need to Know about Lymphedema

World Lymphedema Day is observed annually on March 6 th to raise awareness about lymphedema, a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. How much do you know about lymphedema? In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of lymphedema.
Prevalence of Lymphedema
It is estimated that up to 250 million people worldwide have lymphedema. In developed countries, such as the United States and European nations, the prevalence is estimated to be around 1-2% of the adult population. In some specific populations, such as breast cancer survivors, the prevalence can be higher and range from 15% to 25%.
In developing countries, the rate can be significantly higher, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare, poor sanitation, and high rates of infections.
It is important to improve awareness, early detection, and management of lymphedema globally, with a focus on reducing the burden and improving the quality of life of affected individuals.
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the buildup of lymph fluid in certain parts of the body, typically the arms or legs, but also occurs in the chest wall, abdomen, neck and genitals.
The lymphatic system consists of a network of vessels and lymph nodes that transport lymph fluid throughout the body. When it is impaired or damaged, it leads to the accumulation of lymph fluid in the affected area and causes swelling. That swelling is lymphedema.
What Causes Lymphedema?
Understanding the causes is an important part of preventing lymphedema, especially for people who are at high risk. Here are the risk factors.
1. Cancer
Lymphedema affects a lot of patients with cancer, as cancer treatments like radiation therapy or removal of lymph nodes can interfere with the normal drainage of lymph fluid.
The most studied cancer population for lymphedema has been breast cancer. Experts estimate that from 5% to 40% of women will experience some level of lymphedema after breast cancer surgery.
2. Injury or Trauma
Anyone who has had lymphatic “trauma” is at risk of lymphedema. For example, a car accident, during which multiple structures may be damaged. It might affect lymphatic structures and result in persistent swelling in limbs.
3. Immobility
Movement and exercise can help lymphatic drainage. Reduced mobility can lead to lymphedema because the fluid in the lymphatic system does not get moved along.
4. Obesity
Obesity is a risk factor for many health conditions, including lymphedema. Excess weight can put pressure on the lymphatic system and hinder the proper drainage of lymph fluid, so as to increase the risk of developing lymphedema.
5. Infection
Certain infections, such as cellulitis or parasitic infections like filariasis, can cause inflammation and damage to the lymphatic vessels, resulting in lymphedema.
6. Chronic Venous Insufficiency
When the veins in the legs are unable to return blood to the heart efficiently, it can lead to swelling and increased pressure on the lymphatic system, contributing to lymphedema.
7. Inflammation
Conditions that cause tissue to become red and swollen can also permanently damage the lymphatic system. Rheumatoid arthritis or dermatitis can cause chronic inflammation that can damage the lymphatic vessels and disrupt lymph flow.
Are There Any Early Warning Signs?
Early diagnosis and intervention can reverse mid-lymphedema and help reduce the risk of developing severe lymphedema. Here are some early warning signs of lymphedema. If you notice any warning signs, it is important to see your practitioner or doctor, especially when you are in a high-risk group (check the above risk factors of lymphedema)
The main symptom of lymphedema is PERSISTENT SWELLING, but there are other signs and symptoms associated with the condition.
- Swelling: The affected limbs may appear large or feel heavy and tight due to the accumulation of fluid.
- Restricted range of motion: Lymphedema can cause stiffness in the affected limbs, making it difficult to move or bend joints normally.
- Skin changes: The skin in the affected area may become thickened, hardened, or tight. It might feel warm, tight, or appear red. In some cases, the skin may develop an orange-peel-like texture or small fluid-filled blisters.
- Aching: People may experience discomfort, aching or a heavy sensation in the affected limbs.
- Recurring infections: Lymphedema can make the affected limb more susceptible to infections, causing pain, increased swelling, redness, and fever.
How to Prevent Lymphedema?
Prevention is better than cure. The nature of being uncurable of lymphedema makes prevention even more important. There are several measures you can take to reduce the risk.
- Keep a healthy weight: Obesity can increase the risk of developing lymphedema, so it is important to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Protect your limbs: If you have lymph node removal or radiation therapy, take extra precautions to protect the at-risk limbs from injury, such as using gloves during activities that may cause cuts or scratches and wearing protective garments.
- Gradual increase in physical activity: If you've had lymph node surgery or radiation therapy, it is advisable to gradually increase your physical activity level, ensuring that your body adjusts slowly to avoid excessive strain.
- Proper skin care: Keep your skin clean and moisturized to prevent dryness, itching, and infections. Use a mild, pH-neutral soap and apply a moisturizer regularly. Avoid hot baths, excessive sun exposure, and harsh chemicals that could damage or irritate your skin.
- Maintain good hygiene: Practice excellent hygiene by keeping the affected limb clean, drying it well after bathing, and inspecting for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased warmth.
- Avoid extreme temperatures: Protection from extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can help prevent flare-ups. Use caution when using heating pads, hot tubs, or ice packs, as extreme temperatures can cause blood vessels to dilate or constrict.
- Avoid tight clothing and accessories: Avoid wearing tight clothing, jewellery, or accessories that can constrict blood flow or lymphatic fluid drainage. Opt for loose-fitting, comfortable clothing and accessories when possible.
- Exercise and physical therapy: Engaging in regular exercise and specific physical therapy techniques, such as gentle range-of-motion exercises, can help with lymphatic flow and muscle tone, supporting the prevention and management of lymphedema.
- Elevate the affected limb: Whenever feasible, elevate the affected limb to encourage fluid drainage and reduce swelling. Use pillows or cushions to prop up the limb whenever you are sitting or lying down.
- Seek early treatment: If you notice any signs of swelling, tightness, or discomfort in your limbs, contact your healthcare provider promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment of lymphedema can improve outcomes and help manage the condition effectively.
How to Do Lymphedema Self-Care at Home?
Lymphedema self-care can help you manage your symptoms at home, which is not only convenient but also time-saving and cost-effective. There are self-care practices you can do at home.
Compression Garments
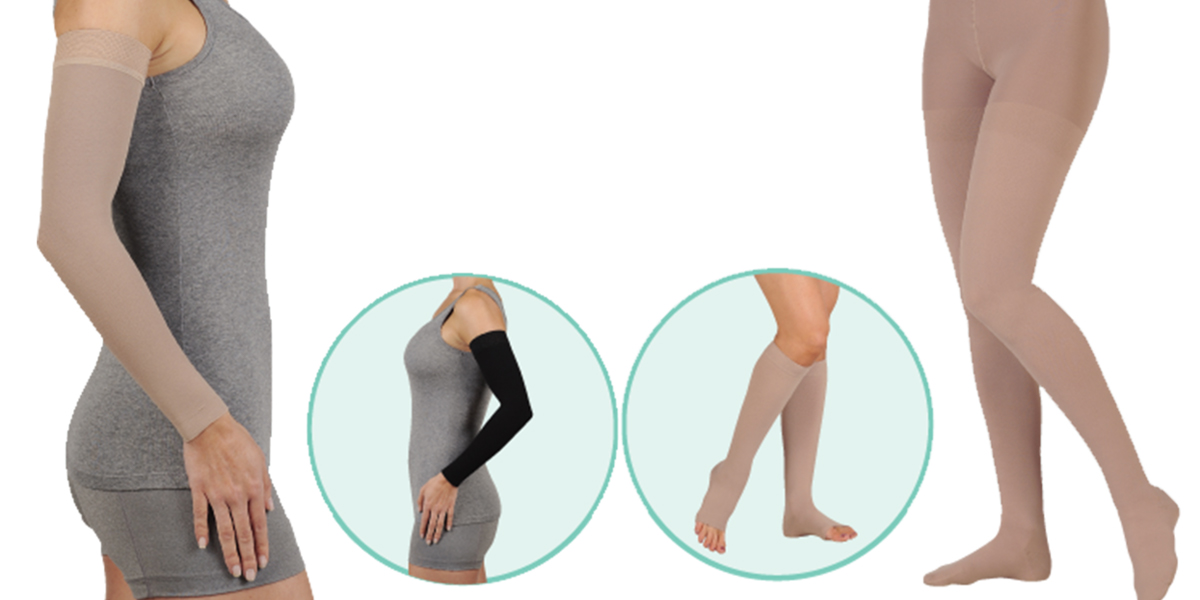
Wearing compression garments is one of the most popular and affordable treatment options. Compression garments apply gentle pressure to the affected limbs which can help encourage the flow of lymph fluid and prevent fluid buildup.
Pneumatic Compression Devices
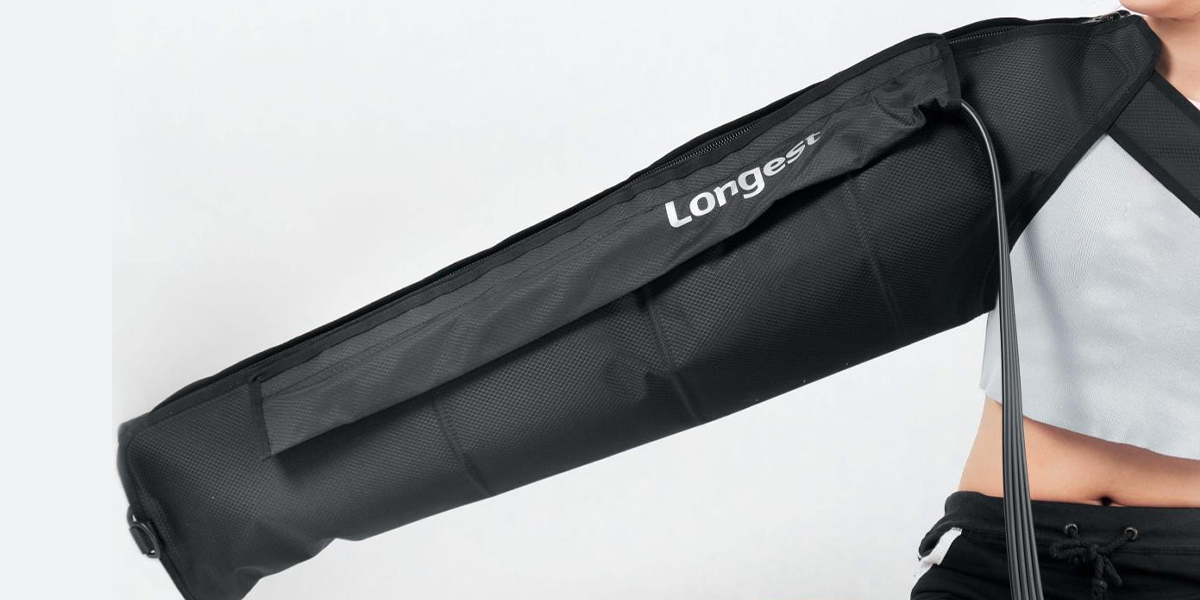

Using a pneumatic compression device to manage lymphedema is an increasingly popular option. It works by applying intermittent and gradient pressure to the limbs to facilitate the flow of lymph fluid.
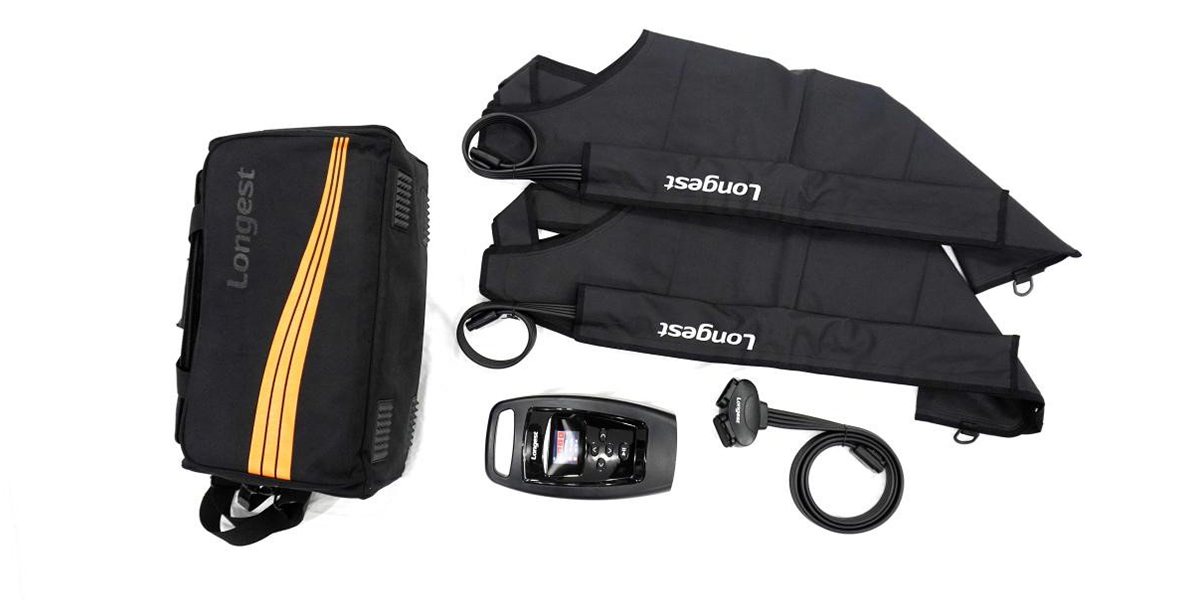

The device consists of an inflatable garment and a control unit that regulates the pressure and timing of compression cycles. It allows for precise control of pressure settings and provides more consistent and higher levels of compression. Pneumatic compression therapy can effectively reduce swelling and pain and prevent the development of fibrosis.
Electrostatic Oscillation Therapy
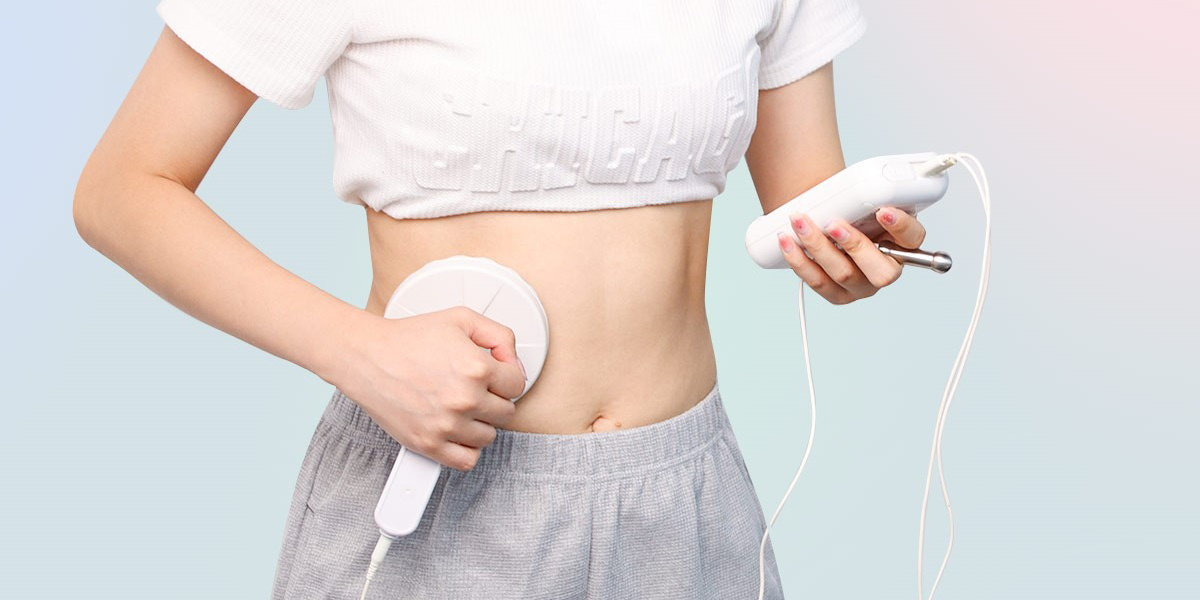

Electrostatic Oscillation Therapy Device PowerOsci LGT-2360S is an innovative treatment technique that has shown effectiveness in managing lymphedema. The therapy involved the application of a handheld device that delivers mechanical vibration to the affected area. These vibrations penetrate deep into the tissues, creating a gentle and rhythmic oscillation. The oscillation can help stimulate the lymphatic system and help improve the flow and efficiency of lymphatic drainage.
In addition, lymphedema often leads to tissue fibrosis, electrostatic oscillations can promote gentle stretching and loosening of the fibre, helping reduce the fibrotic changes and improve tissue elasticity.
Skin Treatment
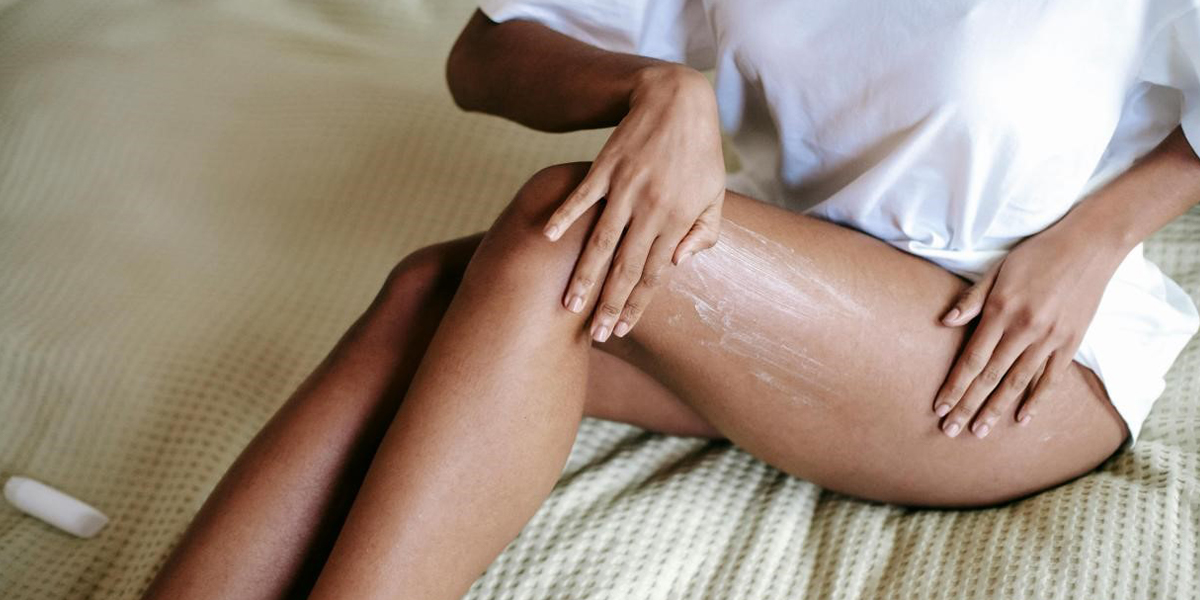

Skincare is an important part of managing lymphedema. Lymphedema makes the skin more susceptible to infection. It is important to make sure your skin is moistured properly.
Exercise
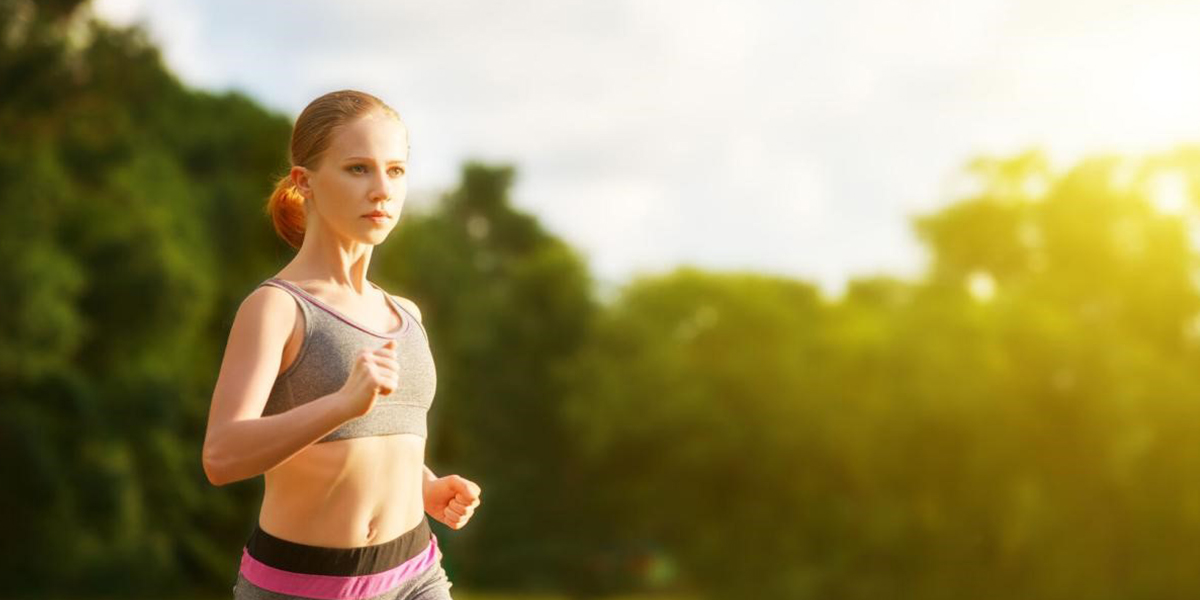

Exercise provides a lot of benefits for your health. And it is one of the easiest ways to manage lymphedema. It can help encourage blood flow as well as lymphatic drainage. Besides, it can help manage your weight.

From "Being Able to Eat" to "Eating Well": Advancing Rehabilitation with Warmth on World Dysphagia Day

Longest Medical LGT-2320 Series Electrotherapy Devices Gain FDA Approval

The Definitive Guide to Shockwave Therapy Machines: Technology, Benefits, and Choosing the Best Device

Unlocking Deep Healing: The Definitive Guide to Focused Shockwave Therapy Machines

Longest Medical Concludes a Brilliant Journey at MEDICA 2025
LGT-2320BE
Are there any side effects of using Electrical Stimulation Machine for aesthetic purposes?
Side effects are rare and minor. They are generally short-lived and resolve on their own. Consult a professional before treatment, especially if you have any concerns or underlying medical conditions.
2520GP
Does your product come with a warranty?
Yes, we're committed to delivering quality products and excellent after-sales service to enhance your overall experience.
LGT-2210DS
Is it suitable for children's use?
Yes, but the sleeves should be customized. MOQ is required.
LGT-2500S - Beauty
In which circumstances is AWT not suitable?
Pregnancy
Over major blood vessels and nerves
Having pacemakers or other implanted devices
Open wounds
Taking oral anti-coagulants Having a blood clotting disorder
Having received a Steroid injection within 6 weeks
Tumors are present at the treatment site
Having skin infection or abrasion at the
Treatment site
Over lung
LGT-2320SP
Is it suitable for all athletes to use the electrical stimulation machine?
Most healthy athletes can generally use it. However, athletes with specific diseases such as heart disease, epilepsy, skin breakage and infection, or those with implanted electronic devices inside the body should not use it. It is essential to consult a professional doctor before use.
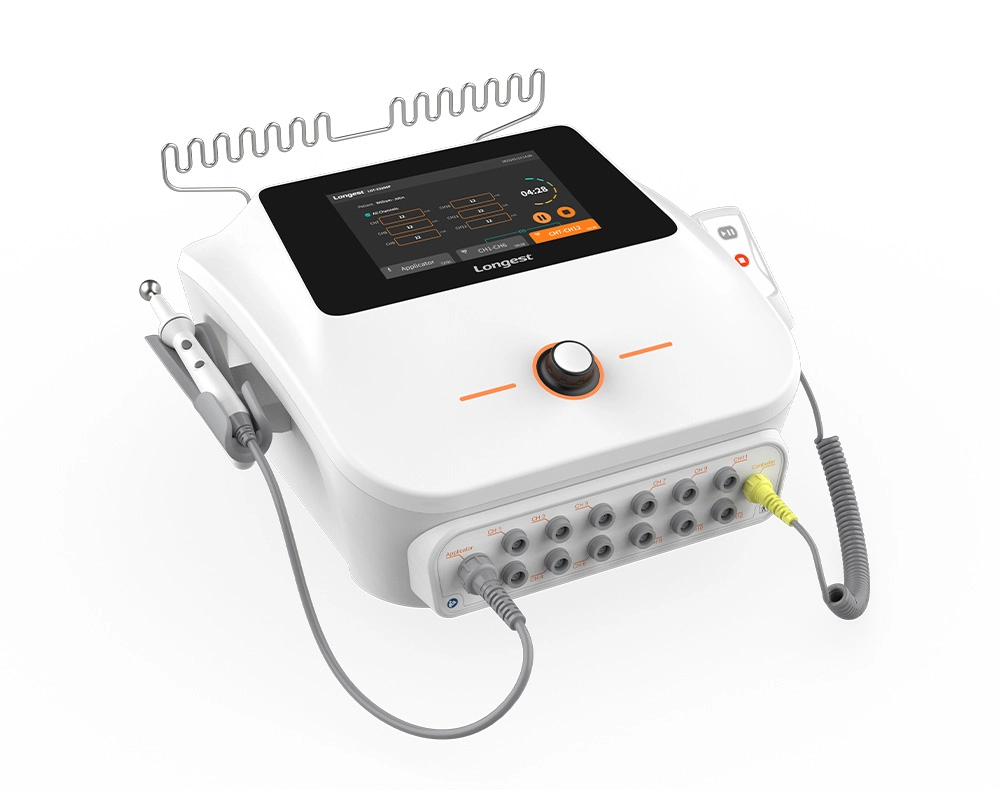

Professional 12-Channel Low-Frequency Electrical Stimulation Machine LGT-2320SP
LGT-2320SP is an advanced electrical stimulation sports training station. It leads to multisite high-efficiency strength gain and realizes bilateral balanced development with motor point detection.
Specifically designed for sports medicine professionals, this device is ideal for the treatment and rehabilitation of sports-related injuries. It delivers precise electrical impulses to targeted areas of the body, promoting pain relief, muscle strengthening, and accelerated recovery.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Pelvic floor rehabilitation LGT-2640AP
The LGT-2640AP Pelvic Floor Magnetic Stimulator is a precision rehabilitation device designed for targeted pelvic floor therapy. Featuring 24 visualized preset protocols (paired with anatomical diagrams), customizable treatment plans, and a pre-adaptation function, it delivers non-invasive, painless stimulation to support postpartum recovery, male pelvic floor rehabilitation, and geriatric pelvic health.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation LGT-2660AP/BP
The LGT-2660 Series Electromagnetic Stimulator for Musculoskeletal Pain is an advanced rehabilitation device engineered to address a wide range of musculoskeletal pain conditions and associated dysfunctions. Operating on the principle of electromagnetic induction, it generates induced currents to regulate neuromuscular function while delivering deeply penetrating energy—this energy transcends superficial tissues to act directly on muscles, joints, and bones. For both acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain, it provides a safe, efficient, and medication-free new solution.

Electromagnetic Stimulator for Body Shaping LGT-2650BP
The LGT-2650BP is a premium unisex body contouring device. Powered by high-intensity magnetic stimulation, it induces intense muscle contractions—effectively boosting muscle tone while reducing stubborn fat deposits. It is widely suited for weight management, body shaping, and individuals with excess weight alike.
Get in touch with us
© 2025 Longest Medical. All Rights Reserved. Powered by gooeyun.






LongestMedical
LongestGloba
longest
guangzhou_longest
GzLongest